Maintaining your income

What is transition to retirement?
Transition to retirement is a strategy that can help you reduce your working hours while maintaining the same level of income. This is achieved by drawing a pension from superannuation using the ‘transition to retirement’ condition of release.
Everyone who is preservation age (currently 55) but less than 65 years of age is eligible to commence a non-commutable allocated pension.
Introducing NCAPs
Non-commutable allocated pensions (NCAPs) have been popular since the federal government’s transition to retirement rules were introduced in 2005. This is because NCAPs allow older Australians access to their preserved super benefits without having to retire.
What are the benefits of this strategy?
Key benefits of an NCAP strategy may include:
- the opportunity to maintain your current income and boost your retirement savings through salary sacrifice (income swap strategy), or
- supplementing your income while reducing your work hours and gradually transitioning into retirement.
How does a transition to retirement income swap strategy work?
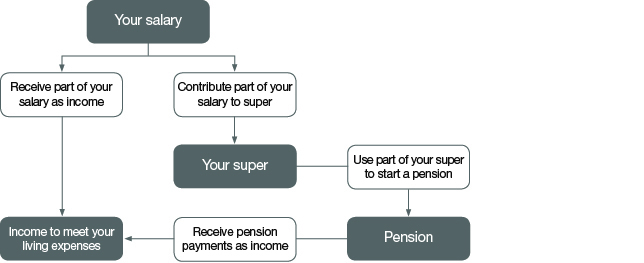
There are two main parts to a transition to retirement strategy:
- Directing a portion of your salary into superannuation, known as salary sacrifice.
- Replacing the income you direct into superannuation with a regular payment from your super savings, otherwise known as a ‘pension’.
A transition to retirement strategy changes the way you receive your income. Instead of receiving your income from one source (your employer), you receive income from two sources (your employer and your superannuation savings).
Can this strategy save you tax?
The benefit of an NCAP strategy comes from the differing tax rates that apply to regular income, superannuation and pensions.
Lower rates of tax generally apply to pension payments received from your super, compared with the marginal tax rates on employment income. This advantage is further increased because any investment earnings in an NCAP will be tax free.
How transition to retirement income swap works
Your superannuation pension is taxed at more favourable rates than your salary. So, by replacing some of your salary with a pension, you can receive the same amount in your pocket while your superannuation savings grow each year.
Pulling it all together
A transition to retirement income swap strategy can be an effective way to boost your superannuation savings. But how much your savings grow will depend on the contributions you make into super through salary sacrifice, compared with the amount you withdraw as your pension. If you take out more money than you put back in, your savings will decline in value. This will result in you having less money to fund your retirement when you stop working altogether.
We can help you strike the right balance and determine whether a transition to retirement strategy is the best way for you to maintain your income and lifestyle as you move towards retirement.
Michael’s story
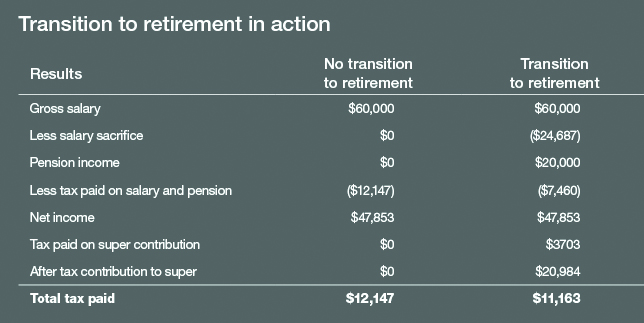
Michael has reached 55 and starts a transition to retirement income swap strategy. Michael’s gross salary is $60,000 per year.
He has accumulated $200,000 in super savings, and elects to use the full amount to start a non-commutable pension, and draws the maximum pension of $20,000.
Together with Michael’s pension income, he can salary sacrifice $24,687 per annum and still receive the same amount of money in his pocket.
After a year, the transition to retirement strategy has resulted in:
- Michael paying $984 less tax.
- An increase of $984 in Michael’s superannuation balance (a withdrawal of $20,000 and an after tax contribution of $20,983.
- The investment earnings that Michael has earned on the $200,000 in his pension account will not be taxed (if these funds remained in his super account, the earnings would be taxed at 15 per cent).
The case study is illustrative only and is not an estimate of the benefits or investment returns you will receive or fees and costs you will incur.
This case study is based on the following assumptions:
(a) Michael beginning a transition to retirement income swap at age 55;
(b) Based on Michael’s gross salary of $60,000 per year, $200,000 accumulated super savings; and
(c) Michael has salary sacrificed to the amount of $24,687 per annum.
This information is correct as of April 2015